Holocaust Timeline
Shoah
Why is the Holocaust significant to the American experience in the Second World War? A young soldier in the 4th Armored Division that liberated the Ohrdruf concentration camp (Germany) had the simple answer when he recalled that day as he entered the camp. "Eisenhower wanted all available soldiers to see why we were fighting here".
A holocaust describes the intentional, catastrophic destruction of a segment of a population. This practice of mass murder, has been a scourge of mankind that began well before recorded history. The systematic, irreparable destruction inflicted on a specific group of people reached its pinnacle in the 20th century, and its devastation was manifest on three continents. The motivation for genocide was deeply rooted in the psyche of the leader of the Third Reich, Adolph Hitler, and predated his rise to power.(1933-1945).
He rose to power with an attractive populist message that struck a chord with Germans whose economic struggles in the aftermath of World War 1 (1914-1918) had left their nation impoverished and impotent on the world stage. Hitler was a charismatic speaker and appealed to his audience by stressing the inherent greatness of the "pure German" and the source that weakened their Aryan blood, the Jew in their midst.
This timeline targets the facts that particularly affected the Jewish population in Germany and in the lands that the Germans occupied in World War 2. We are cognizant that the destruction wreaked on other non Jewish victims would fall within the meaning of "holocaust" (Greek for burning), but the Hebrew "shoah" (catastrophe) points directly to an overarching plan to extinguish Jewish ethnicity. Pope Francis referred to the "shoah" during his historic trip to Israel in 2014 when he met with the few living survivors of the 6 million Jewish dead.
In the case of the non-Jewish victims, many of their deaths were random acts of violence albeit sanctioned by the Nazi government. We note, with sadness, that the victimization of Romani (gypsies) and homosexuals were not ad hoc but also pursuant to a liquidation program.. Our double timeline, one within another, provides the reader with an immediate linear view of significant events that follow the date of inception..
The number of deaths that appear below may appear to be fanciful because of their sheer vollume. However, they were compiled from what the law calls the "best evidence". In this case, the proofs were recorded in the "regular course of business". The meticulous record keeping of Nazi clerks was a prerequisite of the job and a ritual habit of Germans. They were on the scene and collated the raw daily reports in extermination camps and concentration camps. They maintained records of ghetto liquidations. Despite belated attempts of Germans in the field, late in the war, to cover-up evidence of their crimes, their written records appear to have been sacrosanct and preserved for posterity. Additional evidence is adduced from survivors, some with written records, as well as population census reports. Numbers cited are generally "rounded" but well within the actual recorded range of the tragedy. Holocaust/Shoah
Six million murders is a dispassionate summation of the length and breadth of the disaster. This timeline attempts to breakdown that number into its component parts and thereby add a human dimension. Most of the seemingly endless dates represents the imminent death of another innocent victim(s), and with few exceptions, potentially affected the lives of all European Jews.

| Jan 30 | Adolph Hitler sworn in as chancellor of German Republic. |
| Feb 1 | German parliament (Reichstag) dissolved. |
| 22 | 40,000 men sworn in as auxiliary police: SA (brown shirted storm troopers) lost significance by 1939; SS (Schutzstaffel) paramilitary organization led by Heinrich Himmler and held responsible by international tribunal for crimes against humanity. By 1936, actions declared above the law. |
| 27 | Nazis burn Reichstag building and blame communists. |
| 28 | Hitler granted emergency powers. |
| Mar 5 | Nazi party wins 44% of parliamentary vote and by months end granted dictatorial powers. |
| 11 | SA attacks Jewish owned department stores. |
| 20 | 1st concentration opened in Dachau (near Munich). First prisoners are German communists and socialists. |
| 26 | Hitler decrees boycott of all Jewish businesses and immediately implemented. |
| Apr 7 | All non-Aryan teachers and civil service workers dismissed. |
| 11 | Nazis define non-Aryans and eliminate persons with Jewish ancestry of three generations. |
| 25 | Quota for non-Aryan students in schools. |
| May 10 | Books by Jewish authors burned. |
| Jun 3 | Jews permitted to immigrate to Palestine provided all of their assets are deposited with Nazis. |
| 14 | Only Nazi political party permitted. German Jew stripped of citizenship |
| Oct 4 | Propaganda Minister, Joseph Goebbels, discharges all Jewish (non-Aryan) newspaper editors. |
| Feb 5 | Jewish medical students prohibited from participating in licensing examinations. In 4 years, Jewish medical practitioners will be prohibited from treating Aryans. |
| 17 | Jews no longer qualify for national health insurance. |
| Jul | A wave of illegal emigration to Palestine begins for Jews of central and eastern Europe clashing with British prohibitions applicable to the holy land. Cuts in immigration further accelerated in April 1936 when 3 year Arab revolt begins. |
| Aug 2 | German President Hindenberg, a national hero, dies and is succeeded by Hitler with large, popular support. |
| Dec | Hans Frank directed to tailor German law to fit Nazi ideology. In October 1939, he will be appointed governor (Gauleiter) of Poland. |
| May 21 | Jews banned from service in German military. |
| Jun 26 | German women with hereditary diseases forced to abort, but healthy women’s rights for abortion are restricted. |
| Aug 18 | Civil marriages for Jews prohibited. |
| Sept 15 | Nuremberg Laws promulgated: intermarriage prohibited and only Aryans (pure German blood) are citizens of Germany. |
| Oct 10 | Prayers that exalt Jewish spiritual greatness banned from Yom Kipper (holiest day of year in Jewish calendar) services and rabbi arrested for defying ban. |
| Feb 4 | Leader of Nazi organization in Switzerland assassinated by David Frankfurter in protest of Jewish crackdown in Germany. |
| Mar | SS officers to operate concentration camps. |
| 9 | Polish pogrom kills Jews in Przytyk. |
| Jun 17 | Heinrich Himmler appointed to head police. |
| 30 | In Poland, Jews begin strike in protest of anti-Semitism. |
| July 12 | Sachsenhausen concentration camp built near Berlin and housed prisoners of mixed backgrounds. About 35,000 victims died before liberation by Red Army on April 22, 1945. Crematorium built in 1940. |
| Aug 1 | Olympic games in Germany temporarily lowers profile of anti-Semitism but they exclude almost all their Jewish athletes from their teams. Many Americans support total boycott. Avery Brundage, President of American Olympic Committee bans some American Jewish from high profile track team. Two days after the Olympics, Captain Wolfgang Fürstner, head of the Olympic village, committed suicide after he was dismissed from active military service because of his Jewish ancestry. |
| Jan 30 | Hitler conjoins Jews with Bolshevism another Nazi target that appeals to wide German opinion. |
| Mar 15 | Joint Boycott Council stages large rally in New York protesting Nazi government. |
| 21 | Pope Pius XI protests racism. |
| Jul 16 | Buchenwald Concentration Camp opens near Weimar, Germany. While the camp had no gas chambers, according go Nazi records, 56,545 died. The camp was liberated by American Third Army April 11, 1945. |
| Oct 20 | Anti-Jewish violence in Danzig, a free city (under terms of Versailles Treaty WW1) lying on the Baltic sea between Poland and Germany. |
| Dec 28 | Romania installs an anti-Semitic regime and in the new year (January 21) cancels Jewish citizenship and nullifies minority rights. |
| Mar 13 | Germany annexes Austria (anschluss) and their 200,000 Jews are at risk. Two weeks later Jewish community associations no longer officially accepted. |
| Apr 22 | Straw-man fronts for Jewish owned businesses are prohibited. Within a week thereafter, Jews ordered to report all assets paving way for confiscation. In the following month, Jews can longer engage in commercial services and by Dec 3 only Aryans can own a business. |
| Jun 8 | Munich synagogue destroyed. |
| Jul | League of Nations meet in Switzerland to discuss remedy of fleeing German Jews. None of the 32 countries represented will accept the refugees. |
| 23 | Jews 15 years of age and older required to apply for identity cards. |
| Aug 8 | Mauthausen concentration camp was located near Linz, Austria. The camp was surrounded by an electrified fence and witnessed the death of 150,000 victims. The facility was liberated by the U.S. 11th Armored Division in May 1945. |
| 17 | Jewish women required to add the name “Sarah” and men required to add the name “Isaac” stamped in red on all official documents. |
| 26 | Central office for Jewish emigration in Germany led by Adolph Eichmann and in the following year leads same post in Prague, Czechoslovakia. |
| Sep 29 | Jewish lawyers barred from practice in Germany, |
| Oct 28 | 15,000 Jews of Polish extraction deported to Poland who refuses entry leaving the refugees on the border in limbo. |
| Nov 7 | In response to expulsion of Polish Jews, a student, son of a refugee family, assassinates 3rd Secretary in Germany’s Paris embassy. |
| 9-10 | Retaliation: Germans rampage throughout Germany destroying Jewish businesses, loot stores and destroy 267 synagogues. They arrest 30,000 Jews and send them th concentration camps at Sachsenhausen, Dachau and Buchenwald. |
| 10 | Italy issue anti-Semitic racial laws. |
| 12 | German Jews fined 1 billion Reich marks. |
| 15 | Jewish children barred from public schools. |
| Dec 14 | Hermann Göring leads resolution of “Jewish Question”. His first act in January of the new year is ordering Reinhard Heydrich to speed up Jewish emigration. In response, over 27,000 Jews will leave for Palestine in 1939. |
| Jan 24 | Heydrich assumes office of Reich Central office for Emigration. After the invasion of Poland on September 1, he orders the expulsion and forced deportation of Jews to the eastern part of Poland occupied by German troops. |
| 30 | Hitler warns the world that in the event of war he will exterminate the Jews in Europe. |
| Feb 21 | Law confiscates all gold and silver personal property owned by Jews. |
| Mar 4 | Decree provides that all Jews subject to forced labor. |
| 15 | German seizes Czechoslovakia and put 350,000 Jews at risk. Slovakia, in the following month, enacts its version of the Nuremberg racial laws. |
| Apr 30 | German landlords have the right to evict Jewish tenants to be relocated in Jewish houses. |
| May 3 | Hungary bars Jewish lawyers, judges and teachers from pursuing their professions and, within days, prohibits all involvement of Jews in the economic life of the country. |
| The passenger liner, St. Louis, carries 930 Jewish refugees and prohibited to land in Cuba or the United States and forced to return to Europe where they will all perish. | |
| 15 | Ravensbrück concentration camp was located about 50 miles north of Berlin. It was specifically operated for women intended for forced labor. Some were forced into brothels and others into medical experimentation. The camp was liberated by the Red Army April 30, 1945. |
| 17 | British issue the Macdonold “white paper” with further restrictions on Jews to enter Palestine. |
| Jul 4 | German Jews lose all government jobs. |
| Sep 1 | Germans invade Poland and put over 3 million Jews at risk. |
| German Jews subject to night time curfew. | |
| 2 | Stutthof concentration camp opened in the Danzig corridor (free city of Danzig). There were well over 85,000 victims. Many of the prisoners were immediately executed before their arrival was recorded. In 1943, the camp added a gas chamber and a crematorium. The Russian army liberated the camp May 10, 1945. |
| 3 | Britain and France declare war on Germany. |
| 5 | U.S. declares its neutrality. |
| 6 | SS execute Jews in Krakow second largest Polish city located in the south of the country. Ghetto sealed with its 70,000 Jews and by April 12, 1940, Governor Frank declares the city “Jew free”. |
| 9 | Gestapo orders all Polish Jews should be transported to Dachau, Germany.(That will change over tine.) |
| 13 | Germans bomb Jewish quarter in Warsaw, capital of Poland, on Jewish New Year. |
| 17 | USSR invades eastern Poland subject to an agreement with Germany. They occupy Vilna pre war home of 55,000 Jews. |
| 18 | When the Germans occupied Lublin, a city southeast of Warsaw, its Jewish population was about 42,000, immediately pressed into forced labor and wore the obligatory yellow star. In weeks that will be obligatory for all Jews over 10 years old. All synagogues destroyed.Ghetto sealed in April 24, 1941. |
| 21 | Heydrich ordered his SS Eisatzgruppen (special action groups) to press all Jews into ghettos located near railroad tracks a forewarning of imminent transit to “camps”. He also ordered the formation of Judenrat, councils of Jews to help execute Nazi policies. |
| 23 | German Jews prohibited radios. |
| 27 | Warsaw surrenders. Poland follows laying down arms on October 5. |
| 28 | Heydrich centralizes the 3 police units most responsible for terrorizing Europe:SS Security Service (SD), Security Police (Gestapo), Criminal Police (Kripo) |
| Nazis systematically execute mental patients and streamline the process in December with mobile gas vans. | |
| Oct 6 | Eichmann ordered to resettle 80,000 Jews from Upper Silesia (border region between Poland and Germany) followed on October 12 by the deportation of Vienna’s Jews to Lublin, Poland. (See September 18, 1939 above) |
| Hitler proclaims that Jews should be isolated. | |
| 8 | First Jewish ghetto formed in Piotrkow Trybunalski (south central Poland) |
| 26 | Gauleiter Frank orders that all Jews 14-60 must perform 2 years of forced labor. |
| His jurisdiction covers all Polish areas occupied by German troops and not otherwise incorporated into Greater Germany. | |
| Nov 15 | All synagogues in Lodz destroyed. A city in Central Poland with a Jewish population well over 200,000. Following January 31, 20,000 deported and ghetto sealed in April 1940. In April 1940, the ghetto is sealed with its 230,000 Jewish population. False signs were posted advising non-Jews of infectious disease in order to keep them at distance from the ghetto. |
| 29 | Himmler orders all Jews resisting deportation to be executed. |
| Dec 18 | German Jews have rations cut. In following March, cards stamped with “J”. |
| Jan | Start of underground Jewish youth movement in Poland. |
| Auschwitz concentration camp (near Krakow, Poland) begins construction and will be operational May1. Rudolph Höss, Commandant | |
| 1 | 7 crematoria opened in Buchenwald. |
| 5 | Polish Jews subjected to curfew—9PM -5AM. |
| 24 | Gauleiter Frank orders registration of all property held by Jews in occupied Poland (Generalgouvernment) and will prohibit them use of railroads in April. |
| 26 | Warsaw “judenrat” (Jewish council sanctioned by Germans to aid in administration of ghetto) to 100,000 zloty fine for death of an ethnic German. Failure will result in death of 100 Jews. |
| Feb 2 | Tax imposed on emigrating Jews reputedly to cover expenses for Jewish schools and welfare services. |
| 12 | First deportations of German Jews to Poland. |
| 20 | Sachsenhausen (see above July 12, 1936) receive transports from Dachau and Flossburg. |
| 31 | Polish Jewish youth beaten by Polish citizens while German police merely observe. |
| Apr 9 | German invade Denmark (at risk 8000 Jews) and Norway (at risk 2000 Jews).Norway will resist to June. Sweden retains neutral status, but will be a haven for escaping Danish Jews. |
| 23 | Slovak parliament calls for confiscation of all Jewish property. |
| May | Polish underground newspapers, Bulletin and Dror, appear surreptitiously. |
| 10 | Invasion of France (350,000 Jews), Belgium (65,000 Jews), Luxembourg (3500 Jews) Netherlands (of 139,000 Jews most reside in Amsterdam) All will surrender within a month. France will surrender and sign armistice on June 14 on date Paris occupied. Dutch deportations to Buchenwald begin in February 1941. Balance of Amsterdam Jews sent to Auschwitz in February 1944. Some Belgians in Antwerp involved in anti-Jewish riots. First Belgians arrested in September 1943 and sent to Auschwitz. |
| 15 | Round-up of Romani people (gypsies) and deported to Poland. |
| June | Eichmann proposes plan to deport Jews to Madagascar an island lying off east African coast. Original plan investigated by Polish government in 1937 found unfeasible. |
| 17 | The French collaborators setup the Vichy government under Marshal Philippe Petain in the south of France and immediately decree forced labor camps in their Morocco territory for European refugee Jews in North Africa. By October, anti Jewish laws are issued and reinforced with Nuremberg like decrees in November. |
| 28 | USSR annexes eastern areas of Romania. Neighboring Hungary grabs northern Romania (Transylvania) and King Carol flees when fascist government installed. Romania has conscripted slave labor for months. |
| Jul | 4,000 Polish Jews escape into Lithuania. |
| 1 | In Bradenberg, Germany Jewish mental patients gassed. |
| 19 | German Jews lose their telephones. |
| Aug 8 | Romania imposes anti Jewish restrictions affecting employment but are invaded by Germany on October 7. |
| Sep 27 | Tripartite agreement binds Germany, Italy, Japan. They are joined Hungary, Romania, and Slovakia by November; Bulgaria will follow in March 1941 and in February imposes anti Jewish laws. They will be occupied by Germans in March. Romanian oil fields prompt German control. |
| Nov 15 | Warsaw Ghetto seals 400,000 Jews behind 9 foot wall topped with barbed wire and subject shoot to kill orders. |
| 25 | Patria sinks in Haifa Harbor and 250 Jewish refugees drown. British for compassionate reasons permit survivors to entire Palestine. |
| Dec 3 | 3 ships carrying Jewish immigrants to Palestine diverted to Mauritius (Indian Ocean). Most will return to Palestine after the war. |
| Jan | Der Stürmer, Nazi propaganda newspaper, edited by Nazi ideologue, Julius Streicher, calls for death of all Jews. |
| 6 | Romanian pogrom massacres 2000 Jews. |
| Feb 22 | In Netherlands, ethnic German killed and Nazi response is deportation of 400 Jews from Amsterdam. |
| Mar | Auschwitz annex, Birkenau, prepared for extermination services, October construction and operational in January 1942. First “selection” (those chosen for the gas chambers) May 4, 1942. |
| 7 | New conscription of German Jews for forced labor. |
| 26 | SS death squads given free rein in Poland. |
| Apr 1 | Jews in Warsaw ghetto rounded-up for forced labor. |
| 6 | Germans invade Greece and Yugoslavia each with about 75,000 Jews. |
| 7 | 30,000 Jews restricted to Radom ghetto (Poland). |
| May 14 | 3600 Jews arrested in Paris. |
| 15 | Himmler approves medical experimentation in Dachau. |
| 20 | Gestapo prohibits German Jewish emigration. |
| Jun 3 | U.S. State Department institute procedures that will discourage Jewish refugees from German occupied lands. |
| 22 | Operation Barbarossa: Germans attack Russia ( 3 million Jews at risk.) Alfred Rosenberg appointed to administer German occupied land. |
| Croatian Jews deported to concentration camps. | |
| 23 | SS death squads immediately active in USSR. |
| 24 | Jews in Vilna and Kovno aided by local Lithuanians are indiscriminately killed. In Kovno in November 1941, 4934 German Jews held on Kovno ghetto were killed in 5 days. Then thousands of Jews that had no work permit, were killed at Ninth Fort. 500 escape join partisans.Through 1944, 100,000 killed in Vilna area. In July, 1941, the Vilna community was commanded to hand over to the Germans 2 million ruble on penalty of execution of the Jewish Board (Judenrat). Only 50% raised ans 2 Jews shot. On Yom Kippur holiday, Oct 1, 1941, additional 3000 killed. |
| 25 | In Jassy now in Moldova), Romanian Iron Guard murder 10,000 to 15,000 Jews (conflicting records). |
| 27 | SS death squad with aid of Lithuanians kill 2000 in Lusk. |
| 29 | When 760 Jews are killed, Catholic bishop forbids Lithuanian clergy to offer aid. |
| July | Ghettos established in Kovno (Lithuania) Minsk and Vitebsk (Belarus) and in Zhitomer (Ukraine) 10,000 Jews will executed in September. . Minsk held 100,000 Jews. A resistance movement organized escapes and it is estimated that 10,000 were able to join partisan groups. Ghetto liquidated October 1943; 4000 killed. |
| In Riga Latvia, over the course of the month, 18000 Jews killed. | |
| SS death squads eliminate 150,000 Jews on the Romanian border in Bessarabia. | |
| Auschwitz is chosen by Himmler to lead the way in the “final solution”. In September, Zyclon-B gas is tested on Russian prisoners of war. | |
| 7 | In Lvov, Poland 7000 Jews shot. (Now city in Ukraine.) Ghettos established in Lvov and Bialystok, Poland. In Bialystok, August 1943, a group 300-500 Jews ((many members of BOJOWA –Warsaw ant-fascist organization) attacked the German garrison with small arms. They were defeated, but 150 broke free and escaped to a forest and joined partisan fighters. |
| 24 | Kishinev, Bessarabia (now Moldova) was site of the murder of 10,000 Jews. |
| 25 | 3800 Jews killed in Kovno by Lithuanians. |
| Aug | During this month, Romanians turn neighboring Transnistria into a killing field with its 70,000 deported Jews. |
| 2 | Hungarian government prohibits Jews from intermarriage. |
| 5 | During siege of Odessa (Ukraine), 8000 Jews killed. In October 25,000 will be shot. |
| 6-9 | Pinsk, Belarus was occupied by the German forces July 4, 1941. Shortly thereafter 6,000 Jews were shot. The ghetto was established thereafter May 1942. It had a short life and it was liquidated in October 1942. Discovered years later was a detailed census in German naming every individual and age in the ghetto. This is precisely the type of document referred to in our preface that established mortality data. |
| 27-28 | Kamenets-Podolsk (Ukraine) was the scene of the massacre of 23,600 Jews. 14,000 were from Hungary. |
| 31 | Bessarabia during the course of hostilities witnessed 150,000 to 200,000 were murdered; 150,000 were shipped to Transnistria for extermination. |
| Sep 1 | German and Austrian Jews required to wear arm identification arm bands |
| 17 | Large deportation of German Jews to the east. |
| 19 | Kiev, Ukraine captured by German army. Liberated by Soviet army November 1943. |
| 29 | 33.771 Kiev Jews massacred in Babi Yar forest. In 1942, Jewish Sonderkommandos (prisoners who collected Jewish bodies for disposal pursuant to the orders of Nazi guards) ordered to dig up bodies and burn the evidence. Some claims allege as many as 100,000 Jews were murdered. |
| Oct 1 | Under construction, Majdanek camp on outskirts of Lublin Poland operational April 1942 (until liberated by Soviet Army July 22,1944.) Conflicting studies range victims between 75,000-300,000. |
| 8 | Vitebsk is a city in Belarus that borders Lithuania and Russia. Its prewar Jewish population was 50,000. On July 11, the city was occupied by German army. They liquidated the ghetto population of 16,000 and tossed bodies in a river. |
| 10 | Heydrich and Eichmann attend a Prague (Czechoslovakia) conference to discuss the question of the Jewish solution. This city will also be the final resting place of Heydrich who was assassinated there in May 1942 (dies June 4). As a reprisal, Germans liquidate the town of lidice and its inhabitants. His legacy was the Nazi program to liquidate all Jews in Poland----“Aktion Reinhard” was the most deadly period of Jewish extermination between October 1941 and November 1943 resulting in 2 million Polish, Jewish gas chamber victims. |
| 11 | In 1930, the Jewish population of Cernnauti, Romania was 46,000. In 1939, Soviets occupied the city and deported 10,000 Jews to Siberia. In 1941, Germans entered the city and established a ghetto of about 50,000 Jews. Most of the able bodied were pressed into forced labor details. From October through June 1942, 33,000 were deported to the killing fields of Transnistria |
| 15 | Mass deportations of German and Austrian Jews to ghettos in the east. Records note that the Jews from tiny Luxembourg were transported to the Riga (Latvia) ghetto on October 19. That camp witnessed the execution of 10,000-15,000 Jews November 30. Records indicate that Latvian and German Jews were the main victims. |
| 23 | Conflicting records of Jews killed on this date in Odessa (Ukraine) range between 19,000 and 35000. The higher number may have included an infamous march toward the town of Dalnik in November. The Romanian soldiers shot and burned 20,000 Jews on the route of the transport. Romanians had captured the city and set up concentration camps around the city. |
| Emigration of Jews from Germany halted. | |
| 24 | Eichmann approves use of mobile gassing vans immediately upon arrival at ghettos. |
| 25 | Russian army’s stiff resistance to Wehrmacht offense at Smolensk located on Russia’s Dnieper River. Jews in the area arm themselves. |
| 30 | Bratislavia ghetto (Slovakia) begin deportations. |
| Nov | SS death squad (Einsatzgruppe B) deaths accomplished reported for first 20 days of the month: Rovno (Ukraine) 21,000, Latvia 3000, Minsk (Belarus bordering Lithuania) 19000. |
| 20 | Rumbla Forest massacre located near Riga, Latvia. SS Eisatzgruppe A executed 24,000 Latvian Jews, 1000 German Jews aided by local collaborators. |
| 24 | Theresienstadt ghetto (Czechoslovakia) established as a fictionalized settlement where Jews lived under ideal conditions. Used purely for propaganda. On July 2, 1942 , Berlin Jews transported to this camp. In June 1944, the Red cross visits the model village with well rehearsed prisoner population and gets a passing grade for their humane treatment of prisoners. Most will be sent to Auschwitz by December 1944 and replaced by Jews from Slovakia. |
| 30 | Riga, Latvia: conflicting records on Jewish deaths estimate between 10,000-15,000. |
| Dec 7 | U.S. attacked by Japanese at Pearl Harbor and declares war on Japan the next day. Japan’s Tripartite partners, Germany, Italy, declare war on U.S. on December 11, 1941. |
| 8 | Mobile gas vans used at Chelmno (Poland) extermination camp. In January of 1942, 10,000 Jews from nearby Lodz killed. By early April, an additional 30,000 gassed. Camp operated until 1943 and then again from June 23, 1944 to January 18, 1945. Total Jewish deaths----300,000. |
| 12 | The boat, Struma, carrying 769 Jewish refugees sails for Palestine and refused entry by British. They return to their starting point in the Black Sea and sunk by a Russian Submarine February 1942. |
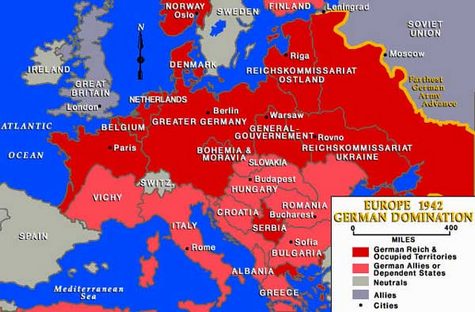
| Jan 2 | Western Crimea (Ukraine) declared Judenrein (Jew free) and entire peninsula free by April. |
| Mass gassing with Zyclon-B in Birkenau and bodies buried in common graves. | |
| 5 | German Jews forced to surrender winter clothes for soldiers on Russian front. |
| 20 | Wannsee Conference (Berlin suburb) coordinates “Final Solution” for Jewish extermination policy already in effect. |
| 31 | SS death squads report card: 70,000 Latvians killed and 3750 slave laborers temporarily survive. The Einsatzgruppe A boasts 229,052 Jews killed. |
| Feb 8 | Salonika (Greece) Jews transported to Auschwitz. |
| Mar 1 | Construction begins for Sobibor extermination camp (SS SoderKommando Sobibor) located in remote area of Poland was ready for transports from numerous occupied countries by May. Its 250,000 deaths resulted from, at first, suffocation in gas chambers from engine exhaust and then changed to Zyclon-B. Shortly after an ill conceived escape plan of 600 in October 1943 (50 escaped) the camp will close. Attempts were made to conceal its existence. |
| 17 | Belzec extermination camp (Lublin District, Poland) started operation 1940 as a forced labor camp. In March 1942, it began systematic extermination with 3 gas chambers that could kill 1200 at a time. It then added another 3 gas chambers. Its guards were a mix of SS and Ukrainians. When they terminated operations in December 1942, 600,000 Jews had been eliminated. |
| 26 | 60,000 Slovakian Jews readied for transport and potential extermination. |
| 28 | First French Jews to be transported to Auschwitz and arrive on the 30th of the month. |
| Apr 20 | German Jews banned from using trains or any public transportation. |
| May 18 | Report funneled from Lisbon and reported in NY Times: 200,000 Jews slaughtered in occupied Russia, 100,000 in Latvia, Lithuania, 100,000 in Poland. Followed by reports from London in June and July that 1,000,000 Jews killed by Nazis. Over the summer, further reports, reputedly a German industrialist the source, of intent to exterminate all Jews, leaks into world Jewish Congress in Switzerland. |
| July 7 | Himmler approves sterilization experiments in Auschwitz which will begin in December of this year. |
| 11 | 9,000 Greek Jews conscripted for forced labor. |
| 14 | Start of deportation of Dutch Jews to Holland. |
| 16 | Drancy camp on outskirts of Paris holds 12,887 Jews. Eventually they will be a collection depot for transport of 74,000 Jews to Auschwitz, Majdanek, Sobibor. |
| 17 | Vichy government enacts Nuremberg type anti-Jewish laws and further similar legislation in October. |
| 19 | Himmler orders all Jews to be exterminated in occupied Poland (Operation Reinhard) by end of year. |
| 20 | Unsuccessful uprising in Nezvizh ghetto (Belarus) during liquidation. |
| Uprising in Tuchin ghetto (Belarus) where Jews burn their own houses and escape to woods. Local Ukrainians hunt them and turn them over to Germans. | |
| 21 | Mass demonstration in New York Madison Square Garden protesting killing in Poland. |
| 22-23 | German ready Warsaw ghetto Jews for transport to new Treblinka extermination camp north- east of Warsaw. 800,000 will die in the gas chambers. Carbon monoxide gas is replaced with Zyclon-B following the lead of Auschwitz. Over 10,000 will die from summary executions, starvation and disease. Two camps were constructed. One camp was strictly used for extermination with the exception of sonderkommandos (slave laborers) used for burial details by burning in open pits. The other camp used Jewish slave labor to cut trees in nearby forest to fuel the crematoria. In August 1943, the sonerkommandos revolted and killed some few Nazi guards. Seventy were able to escape. The advent of an advancing Soviet army in 1943 forced the closure of the camp. |
| Belgian Jews transported to Auschwitz. | |
| The head of the Judenrat (Jewish administrative council sanctioned by the Germans) commits suicide rather than participate in Nazi transport program. | |
| 28 | ZOB- Jewish resistance force formed in Warsaw ghetto. |
| Aug | Croation Jews shipped to Auschwitz. |
| 8 | Romanians promulgate anti-Jewish laws. |
| 10 | Jewish partisan brigade attacks Germans in Belarus. |
| 11 | U.S. State Department received information of German plan to exterminate Jews. |
| 26 | 7,000 French Jews arrested in Vichy France. |
| Sep 3 | Unsuccessful armed Jewish resistance to prevent liquidation of Lachva ghetto (Belarus). |
| 26 | The SS controlled all of the concentration camps. They confiscated and collected Jewish valuables particularly on the day of their arrival in a camp. One source estimates that by 1943 the property filled 800 boxcars from Auschwitz. |
| Oct 5 | Himmler orders all Jews in German concentration camp to be transported to Auschwitz and Majdanek camps. |
| 9 | Italy imposes anti-Jewish laws in Libya. |
| 12 | On the eve of the liquidation of Jews in the Mizocz ghetto ( eastern Poland and now part of western Ukraine) Jews rose up and fought for survival over 2 days. Then the survivors were all shot. |
| 16 | Roman Jews transported to Treblinka. (See July 23, 1942) 1000 more will be transported to Auschwitz 1 year later. |
| 22 | 29,000 Jews living in Alsace-Lorraine, Baden and Saar are “relocated” to Vichy, France. |
| Jews in Sachsenhausen camp fight to resist transport to Auschwitz. | |
| 25 | Auschwitz busy receiving Norwegian Jews and 3 days later a group from the “model camp” of Theresienstadt. |
| Nov | 170,000 Jews in Bialystok area massacred. (See July 7, 1941 above.) |
| Soviet army begins counter offensive in Stalingrad that will change Allied fortunes on the eastern front. | |
| Krakow (Poland) ghetto seals 70,000 Jews which was first established by the Germans on March 3,1941. The ghetto packs in the Jews in a sealed enclave containing about 3000 rooms. The ghetto was located in an industrial neighborhood that included the Schindler factory using the forced labor from the ghetto. Schindler was immortalized as a savior of many Jews by the Spielberg movie, Schindler’s list. His memory is honored in Israel as a “Righteous Person”. | |
| 9 | Germans occupy Tunisia (North Africa) and in December draft Jews for forced labor. In May 1943, Allies retake Tunisia. |
| Dec | In London, the House of Commons is advised by Foreign Minister Anthony Eden that Hitler is actively engaged in exterminating European Jewry. |
| Jan | Himmler orders another 8000 Warsaw ghetto Jews to be deported. On June 11, he orders the total liquidation of all ghettos in occupied Poland. |
| The SS death squads’ toll of Jewish deaths will exceed 1 million in 1943. | |
| 10 | The Jewish resistance groups (ZOB and Youth Group) in Warsaw ghetto prepare a resistance and take first action by January 18. |
| 14 | Roosevelt and Churchill meet in North Africa (Casablanca) and agree on policy of German unconditional surrender. The Jewish question is not on the agenda. |
| Feb | Romanians propose to release 70,000 Jews for deportation to Palestine. This message to Great Britain is ignored. |
| 2 | German army surrenders at Stalingrad. This Russian victory stems German tide. |
| 5 | German liquidate Bialystok (occupied Poland) amidst 1 week of Jewish armed resistance in which 2,000 Jews die. 10,000 transported to Treblinka and are gassed. By August 18, another deportation is interrupted and crushed. Thereafter, all transports sent directly to the Treblinka and Majdanek death camps in Poland. |
| 24 | Salonika; Greek Jews forced into ghetto and in following month first deportation to Auschwitz. By august 18, another shipment there of 43,000 Jews. |
| 27 | In Berlin, Jews laboring in war industries transported to Auschwitz. |
| Mar | Jews in Thrace (Balkan’s region) sent to Treblinka. |
| 17 | Bulgaria opposes deportation of its Jewish population and disperses them to the rural provinces. |
| 22 | Three new gas chambers added in Auschwitz during balance of the month and completed early April. The 4th chamber completed in June. Camp capability-4756 corpses daily. On October, Yom Kippur, thousands of Jews gassed in Birkenau (auxiliary camp to Auschwitz). |
| Apr 19 | Passover eve: Germans begin liquidation of Warsaw ghetto but meet month long armed resistance during which 50,000 Jews died. Mila 18 command bunker falls on May 8. The novel, Mila 18, by Leon Uris memorialized the battle. |
| 20 | A few Jews escape Vilna ghetto and join partisan fighters in the forest. |
| May 7 | Novogrudok (Lithuania): Dates for German activity are conflicted. Some date the earliest “Aktion” of the SS death squad #8 as late as July but the numbers are incontrovertible. Once again local Lithuanian policemen participated in the murders. The first action involved shooting 50 Jews. The next involved the murder of 7.000 Jews outside the city. Some 1,200 Jews survived hiding in the forest, but only 15 families lived in the city after the war. |
| 19 | Berlin declared Judenfrei. |
| 30 | Dr. Josef Mengele arrived in Auschwitz to head its medical personnel. He is known as the “angel of death”. During the “selection” process for new arrivals he would separate some Jews for labor and others for immediate death in a gas chamber. He also conducted medical experiments resulting in deaths of “patients”. He was charged as a war criminal but escaped to South America where he avoided capture and reportedly died in 1979. |
| Jun 2 | Nazis institute policy of burning corpses to hide evidence of atrocities. |
| 11 | Himmler orders liquidation of all Polish ghettos in occupied areas. Later in that month extends the order to Russian occupied territory. |
| Jul 9 | Allied troops invade Sicily. |
| Aug 16 | Bialystok ghetto liquidated. |
| Sept | Minsk and Vilna ghettos eliminated. |
| 11 | Germans occupy Rome (35,000 Jews at risk). In October, 1000 Jews sent to Auschwitz. |
| Jewish families en masse shipped to Auschwitz from Theresienstadt. | |
| Oct 1 | Danes gather over 7000 Jews and save them from deportation and safely ship them to neutral Sweden. |
| 9 | Jews of Trieste rounded up bound for Auschwitz. Further south in Italy in November, Jews in major cities arrested. |
| 14 | Resistance in Sobibor camp (see March 1, 1942 above) and similar rebellions in Treblinka camp, Warsaw, Bialystok, Vilna ghettos leads to the Nazi program dubbed “Operation Harvest Festival”. This action will liquidate the slave laborers in Trawniki, Poniatowa and Majdanek camps. Estimated 40, 000 deaths including the 18,000 killed in 24 hours at Majdanek camp. |
| 20 | United Nations War Crimes Committee formed to investigate and prosecute war criminals. |
| Nov 17 | Jewish partisans liberate Jewish prisoners at Borshchev one of the 32 ghettos set up in Galicia (Ukraine). During the period of Hungarian occupation, their army officers protected the Jews. Under Nazi rule, with the aid of local Ukrainians, 300,000Jews were killed between July 1, 1941 and March 1942 (see above) when Belzec was utilized for extermination. |
| Dec 1 | Italian police order all Jews to be deported. |
| 2 | Auschwitz is the destination for the first transport of Viennese Jews. |
| Jan 3 | Russian forces reach Polish border. |
| 16 | U.S. Treasury officer, Josiah Dubois, reports to White House the State Department attempts to hide plight of Jews. |
| 25 | Gauleiter Hans Frank’s diary entry reports that “ perhaps 100,000 Jews” left in his jurisdiction—occupied Poland out of original population of 2.5 million. |
| 26 | President Roosevelt orders the formation of War Refugee Board to take “all measures—to rescue the victims of enemy oppression”. |
| Feb 2 | The Board extends proposal to neutral Spain to relax border restrictions for refugees, but the American ambassador to Spain (Carlton J.H. Hayes) rejects the plan and makes no attempt to present it to the Spanish government. |
| Mar 9 | Himmler consents to releasing some Jews from camps for slave labor for German industry. |
| 19 | Germans occupy Poland (725,000 Jews at risk) and Eichmann sends in his special SS forces. |
| 24 | President Roosevelt condemns the Germans and Japanese for “crimes against humanity”. |
| He further condemns Hungarian government for harsh measures against Jews. Hungarians ignore the condemnation. In April, they confiscate Jewish property, enforce wearing of Jewish Star, mass shipment of Jews to Auschwitz. Between May 1 and July 9, 454, 551 Jews gassed at Birkenau. Remaining Jews in Budapest kept in marked buildings. | |
| Apr 7 | Two Jewish prisoners of Auschwitz escape and make it to Czechoslovakia (about 250 miles) where one is able to pass information of the mass slaughter to a papal representative. This information is passed to western embassies in Switzerland. |
| 14 | Allied aerial photos taken of Auschwitz while photographing nearby industrial facilities. At the same time, 5200 Greek Jews arrive. Despite hard evidence of gas chambers and crematoria, US War Department (June 29) refuses to bomb the camp although they do bomb nearby industrial sites on August 25. |
| 25 | Eichmann proposes an exchange of Jews for 100,000 trucks. No deal is struck with the Budapest, Jewish Rescue Committee. |
| May 3 | Jews from Transylvania arrive at Auschwitz. |
| 15 | Himmler directly orders the extermination of Hungarian Jews in Auschwitz. Eichmann personally directs gassing of 100,000 Jews by May 24. 380,000 Hungarian Jews arrive by end of June. Over 9,000 Jews will be gassed on one summer day and reportedly exceed the capacity of the crematoria. |
| Jun 6 | Allies land in Normandy to begin assault on continental Europe. |
| Jul 5 | Soviets liberate Minsk and in the same month liberate Vilna with Jewish partisans participating with the Red army. Vilna survivors about 2500 out of original population of 35,000. |
| 7 | Hungarians pressured by international community halt transports but Eichmann ignores the government and ships 1450 Jews Auschwitz on July 19. |
| 8 | Kovno ghetto liquidated. 90 survive. (See June 24, 1941 above) |
| 9 | Swedish diplomat, Raul Wallenberg arrives in Budapest and credited with saving 100,000 Jews. He will disappear in January 1945 arrested by Soviets. |
| 20 | Attempt to assassinate Hitler fails. |
| 2000 Jews from the Greek island of Rhodes transported to Auschwitz. | |
| 24 | Over the next week, Soviets sweep west and liberate Majdanek deep in corpses (360,000 murdered), Lublin and City of Lvov where no Jews are alive of pre-war population of 110,000. |
| 30 | Time for retreating Nazis to liquidate Lodz. |
| Aug 4 | Anne Frank and family arrested in Amsterdam after hiding for years. She is sent to Auschwitz and then to Bergen-Belsen where she dies on March 16, 1945. |
| 6 | Polish ghetto at Lodz liquidated. 60,000 Jews shipped to Auschwitz. |
| Sep 3-5 | In Belgium, Brussels liberated and many hidden Jews of the 27,000 still alive. Jews of Antwerp not the fortunate. Very few alive of pre-war population of 50,000. |
| Oct 7 | Sonderkommando revolt in Auschwitz and crematorium iv destroyed. |
| 15 | Final transport of 2000 Jews from Theresienstadt gassed. |
| 30 | Gas chambers closed at Auschwitz and attempts made to hide evidence on direct orders of Himmler November 25. |
| Nov 8 | 25.000 Jews forced into 100 mile march from Budapest to Austrian border. A second march of 50,000 ends at Mauthausen camp (see August 8, 1938 above). |
| Jan 1 | Hungarian fascist party, Arrow Cross, murders Zionist leader of Hungarian Relief and Rescue Committee. |
| Jan 6: Budapest---Red Army frees 80,000 Jews | |
| 10: Buchenwald ---Allied Army | |
| 15: British liberate Bergen-Belsen and 40,000 Jews freed but evidence of thousands Jews dead on a death march away fro the camp. | |
| 17: Warsaw---Red Army (few Jews out of 450,000 left alive) | |
| 19: Lodz liberated by Red Army | |
| 23 | Soviets on outskirts of Berlin and city surrenders on May 7. |
| 26-29 | Death march from Stutthof camp and 7000 murdered. Soviets hide evidence until 1998. |
| 27: Auschwitz liberated---2,000,000 murdered, 1,500,000 Jews. However, on January 18 the Nazis force march 66,000 prisoners from the camp and shoot the sick enroute. | |
| Feb 1 | Forced march of 40,000 prisoners from Gross-Rosen and thousands die. |
| Mar 16 | Himmler prohibits further atrocities. |
| Apr 4 | Ohrdruf camp liberated and General Eisenhower inspects and angered by the corpses and living dead. |
| Apr 12 | President Roosevelt dies. |
| 15 | British liberate Bergen-Belsen and 40,000 Jews freed but evidence of thousands of Jews dead on a February death march away from the camp and evidence hidden by Soviets until 1998. |
| 29 | U.S. Army liberates Dachau. |
| 30 | Hitler and Eva Braun commit suicide in Berlin bunker. |
| May 2 | Red Cross takes possession of Theresienstadt “model” camp. |
| 5 | Mauthausen liberated. |
| 7 | Germany unconditionally surrenders. |
| 9 | Göring captured by Americans. |
| 23 | Himmler commits suicide while held by British. |
| Nov 20 | Nuremberg trial opens and on the following day Robert H. Jackson opens the case for the prosecution. |
History of American Wars > Holocaust