World War 1 Tanks
1914-1918
There is a gathering consensus among historians that the introduction of the "landship" on World War 1 battlefields was an answer to the trench warfare stalemate. This meant adding greater mobility on the battlefield. Troops could rise out of their trenches and follow behind the metal giants that would lead the way through enemy barbed wire and shield the infantry from withering machine gun fire.
However, ten years prior to the war there were inventive minds that envisioned a motorized, armoured vehicle as an assault weapon, a mobile artillery platform, and not only as a tool for the infantry. In 1904, motorized cars were still a rarity, but engineers in Britain envisioned a larger engine to power a vehicle with mounted guns that could traverse inhospitable terrain. Essentially, a moving fort. The farm tractor was an ideal starting point. Their tracks operated against their built-in climbing face. The earliest tractor models were steam driven and useful in agriculture for threshing.
world war 1 tanks

Converting the tractor for military use had a bumpy start. There were several demonstrations in 1907, 1908 and 1910 presented to the British Mechanical Transport Committee. King Edward attended one such event in 1908 and viewed a tractor in operation with a mock-up of a mounted gun. There was some interest in the concept, but the Royal Artillery officers were unimpressed and their negative appraisal won the day.
By 1915, a year into the war and the forces of both sides were so static that there were conversations between the opposing trenches. The battlefields were severely cratered by opposing bombardments from the large guns, but those guns could not be moved to forward positions because of the deep depressions and muddy ground conditions. That would rule out wheeled vehicles. The British sought tractors to pull the guns. However, the British owner of the patent, discouraged, had sold his rights to the American Holt Company---predecessor of the current, giant Caterpillar Inc. whose named was first coined by British soldiers. The British ordered the tractors from the Americans and this engendered a second look at the possibilities of the tank.
World War 1 Tanks
|
The Holt tractor in its original military use as transportation for big cannon at Vosges, France in 1915. The advantages of the Holt tractor would be incorporated in all British Mark tank designs and almost simultaneously in the French version. |
 |
Winston Churchill, first Lord of
the Admiralty, surprisingly presenting a war plan for the army, formed the Landship Committee to
conduct trials for the development of "Little Willie". This was a line of Mark
vehicles l through V that were forerunners of the tank. The "Little Willie" was ready for tests in 1915 with emphasis on its ability to pull loads on the scarred battle fields. The major setback was its poor ability to cross trenches. Engineers would solve that problem with the next generations of "Big Willies" and ultimately in the Mark IV line.
World War 1 Tanks World War 1 Tanks
 |
 |
The secrecy around the trials led to calling the vehicle a "tank" a term never before used. The first order rolled off the assembly line of Foster & Company, an agricultural equipment manufacturer, in February 1916.The Mark I was built low to the ground, and the 28 ton, armoured body was spread over a 26 foot length. There was a female (no side cannon) model that carried a crew of eight that manned 4 Vickers machine guns and one 8 mm Hotchkiss machine gun. The male model (side cannon) had a compartment on each side of the tank . Each housed a 6 pounder cannon. The fire power also included 3 additional Hotchkiss guns.
World War 1 Tanks
|
The Mark I appeared for the first time in 1916 at the Battle of the Somme in the northern part of France---the central part of the infamous western front. Only 9 of some 40 tanks reached enemy lines. Their attack was moderately successful, but their dispersion over a wide front blunted the strategy. The rear wheels were attached for navigating the tank. The vehicle was plagued with mechanical difficulties. It became stuck in large bomb craters, ventilation was lacking and called for further refinements. |
 |
Although Great Britain and France were closely allied, and operated with integrated forces, there does not appear to have been cooperation between them in the development of the tank. However, France also was proceeding with tank development. Their vision was to use the tank as "assault artillery" to clear the field ahead as the infantry would advance behind its bulk.
The French referred to the tank as a "land battleship" (cuirrasse terreste). They and their allies made every effort to produce a viable armored weapon to support their infantry. Not so for the Germans and their Triple Alliance allies. The Germans built some tanks, but their focus was on anti-tank guns.
France was conducting experiments to create their "Land Battleship". In 1914, a farsighted Colonel Jean Baptiste Estienne noted:
"Victory in this war will belong to the belligerent who is the first to put a cannon on a vehicle capable of moving on all kinds of terrain".
The French understood the need for mobility in a modern war. They had drafted 10,000 conscripts with transport for about 4,000 men. Problem solved: Six thousand were sent to the front in Parisian taxis made by Renault. That company would introduce the best tank of the war.
By the spring of 1915, they produced a battleship. The Frot-Laffley was a giant armoured vehicle that was so immobile that it had no battle field utility except as a barbed wire cutter. In the same year, they had to abandon their electrically powered vehicle that required an electric supply cable. This led them to an internal powers supply and a tractor base.
World War 1 Tanks World War 1 Tanks
 |
 |
The French had finally understood that the tank required continuous tracks--tank treads. Late in December 1915, they began using the Holt tractor base concept. Within months they ordered the production of 400 tanks from their domestic Schneider & Co. factories. They produced the CA1 and in quick succession the quite modern St.Chamont. Ultimately. they would outproduce the British.
World War 1 Tanks World War 1 Tanks
 |
 |
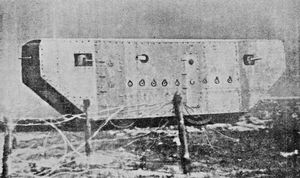
The Germans were on the cutting edge of military technology but made a poor attempt to produce a workable battle tank . Their efforts were aimed at anti tank warfare and a trench weapon capable of penetrating the enemy tank. ( Mauser guns)
Their singular effort in 1918 was the A7V with a speed of 3 mph. The behemoth carried a complement of 18 and a 57mm cannon. The Germans built only 20 and added to that small force some 50 tanks captured from the British. In contrast, the British Mark IV was manned by an 8 man crew.
World War 1 Tanks

German A7V
click to enlarge
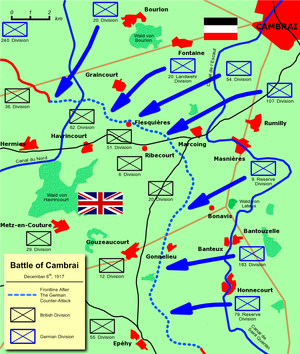
In 1917, British General Alexander Haig concluded that tanks were best utilized en mass rather operating in small isolated group as at the battle of the Somme. At Cambrai, 400 tanks gathered for an attack in groups of 120 in teams of three. The Mark IV was the featured tank. British planes flew overhead to muffle the sounds of the gathering tank corps. It was now considered an independent arm of warfare. Below are German soldiers with captured Mark IV.
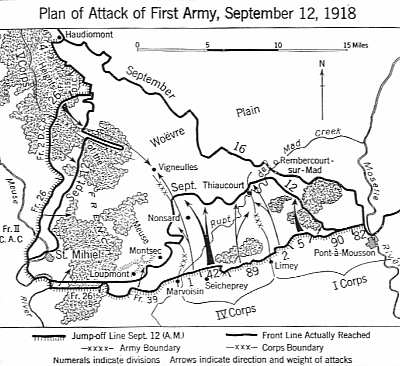
When the United States army reached Europe, they had no American made tanks. The commanding general of the American Expeditionary Force (AEF), John Pershing witnessed a successful tank assault at Cambrai, and was impressed with its potential. He assigned a young Lt. Col. George S. Patton to form a tank corps. Patton rapidly formed training schools in England and France. They were battle ready by September 1918. The American tank crews were now operating the light (8 tons)French Renaults with a 2 man crew and a small number of the British Mark V. Three tank brigades were organized.

Not only were the potential strengths for utilizing tanks noted at Cambrai, their weaknesses were also disclosed. A major problem was the light armor that exposed the tank to enemy artillery and rifle fire. World War 1 Tanks
|
The Renault FT-17 revolutionized tank design. It had a fully rotating turret armed with a 37mm cannon, and carried at least one machine gun with a 2 man crew. Uniquely, the motor was now located at the rear. These features have survived in the present day tank. The cannon replaced the longer barreled naval guns. This eliminated the danger of the nose of the cannon getting stuck in the mud when the tank dipped into a trench or crater. |
 |
The British may have noted the superior mobility of the lighter tank, and in 1917 introduced the Mark A Whippet. This tank could move at 10MPH and carried a weight of about 14 tons. It required a three man crew along with 3 Hotchkiss machine guns.
World War 1 Tanks

The first independent AEF action of the war, under American command of John Pershing, was fought in September 1918 at St. Mihiel south of Verdun. In addition to the U.S. infantry, Patton led the tank assault on the retreating German forces. The western front was finally cracking and U.S. troops were on their way to the famous Argonne Forest battle. Patton, with tank lessons learned, would again confront the Germans in World War II.
Click to enlarge
In this final year of the war, the French used 480 Renault tanks at the battle of Soissons and aided in halting a German drive on Paris.The Renault participated in over 4,000 actions with a loss of 736 tanks.
World War 1 Tanks World War 1 Tanks
 |
 |
In March 1918, the Germans began their spring offensive. Their major target was Amiens, a key supply point for the allies on the western front. The Germans were driving against the village of Villers-Bretonneux ( April 23) to gain the road just east of Amiens. Within a day, the town fell.
A nearby squad of 3 Mark IV tanks were ordered to halt the advance of the German infantry. The tanks were hidden in a forested area, but were spotted by German air observers. They immediately started to take artillery fire. The tanks were forced to maneuver which prevented the male from using its cannon effectively. The 3 tanks, all with disabled crews, began to move forward against the enemy infantry. They immediately met 3 huge German A7Vs. Lt Frank Mitchell noted that his female tank partners had been hit and were withdrawing. When the firing began, inexplicably two of of the A7Vs began to withdraw.

Mark IV
Mitchell halted his tank in order to provide his gunner an opportunity for a clean shot. One of its shells upended the A7V forcing its crew to abandon their tank. A German plane dropped bombs which missed but forced his tank to stall. Their tank was now attacked by the German infantry and their armor piercing bullets were hitting home. The tank restarted but his crew were now at the mercy of the advancing infantry.
Suddenly, 7 Mark A Whippets raced to the rescue and tore into the infantry with heavy machine gun fire. Mitchell kept advancing until he was engaged by another A7V and they began a fire fight. An artillery shell ended the day for the Mitchell tank.
The Germans that escaped the Whippet force were exceedingly fortunate. On the night of April 24, Australian forces reoccupied Villers-Bretonneux and Amiens remained in French hands. Frank Mitchell was awarded the military cross for bravery.
 A7V Mark A Whippet |
 |
_____________________________________________________________________
References and Sources:
American Military History, John W, Chambers. Ed., Oxford University Press.New York 1999.
Complete Encyclopedia of Arms & Weapons, Leonid Tarassuk and Charles Blair.SimonSchuster,NewYork 1999. Department of Air Force
Heyman, Neil M. World War 1,Greenwood Press, Westport, Ct 1997.
Imperial War Museum
Library of Congress
National Archives
Neiberg, Michael Fighting the Great War, President and fellow of Harvard College, 2005.
Reilly, Ralph. Reiley's @ world net.att. net
The Dictionary of the First World War, Stephen Pope and Elizabeth-Anne Wheal, St. Martin's Press, New York 1995.
The Encyclopedia of World War I, Spencer I. Tucker Ed. ABC-CLIO 2005
U.S. Air Service
Wikipedia
Williamson Murray, "Armored Warfare: The
British, French, and German Experiences," in Murray, Williamson; Millet,
Allan R, eds. Military Innovation in the Interwar Period. New York: Cambridge University Press 1996.
World Almanac, David R. Woodward, Facts on File New York 2009.
YouTube
History of American Wars | Causes of World War 1 | World War 1 Tanks